Information system analysis and design is a complex, challenging & stimulating organizational process that a team of business & system professionals uses to develop & maintain computer-based information systems. The analysis & design of an information system is driven from an organizational perspective.
Organizations can respond to & anticipate problems & opportunities through innovative uses of information technology. Information system analysis &design is, therefore, an organizational improvement process. The system is built & rebuilt for organizational benefits.
Information System Analysis and Design
Benefits result from adding value during the process of creating, producing and supporting the organization’s products & services. Thus, the analysis & design of information systems is based on your understanding of the organizations objectives, structures & processes all well as your knowledge of how to exploit information technology for advantage.
System analysis & design is performed by the system analysts to analyze data input or data flow systematically, to process or transform data, to store data & output information in the context of a particular business.
System analysis & design is used to analyze, design & implement improvements in the support of users & the functioning of businesses that can be accomplished through the use of computerized information systems.
Installing a system without proper planning leads to great user dissatisfaction & frequently causes the system to fall into disuse. System analysis & design lends structure to the analysis & design of information systems.
The Need for System Analysis & Design.
It can be thought of as a series of processes systematically undertaken to improve business through the use of computerized information systems. System analysis & design involve working with current and eventual users of information systems to support them working with technologies in an organisational setting.
User involvement throughout the systems project is critical to the successful development of computerized information systems.
System analysis & design involves working with current & eventual users of an information system to support them in working with technologies in organizational settings. User involvement throughout the systems project is critical to the successful development of computerized information systems.
Today, there is more emphasis on working with software users; on performing analysis of their business problems, & objectives & on communicating the analysis & design of the planned system to all involved.
What is System?
A system is an array of components that work together to achieve a common goal by accepting input, processing it, and producing output in an organized manner.
For Eg. The computer is a system with physical components, keyboard, monitor, memory chips, circuits & connecting cables & the basic goal is processing of a data.
Accounting is a system with elements journal, ledgers, people & basis goal is a recording of financial transactions, preparation of balance sheet and reporting on financial operations of an entity.
The human body is a system with elements organism, tissues, bones, blood, nerves network & basic goal is homeostasis.
Characteristics of a system:-
-
Specific Objectives:
The basic objective of a system is to achieve some goal.
For Eg. The objective of a business system is profit making & the objective of an educational institute is to provide better education & the objective of a hospital is to provide better service to maximum patients.
-
Components:
These are the subsystems which collectively function to achieve goals of the system.
For Eg. Accounting system consists of several subsystems like accounts payable, accounts receivable, a general ledger, report generator, etc.
-
Organization:
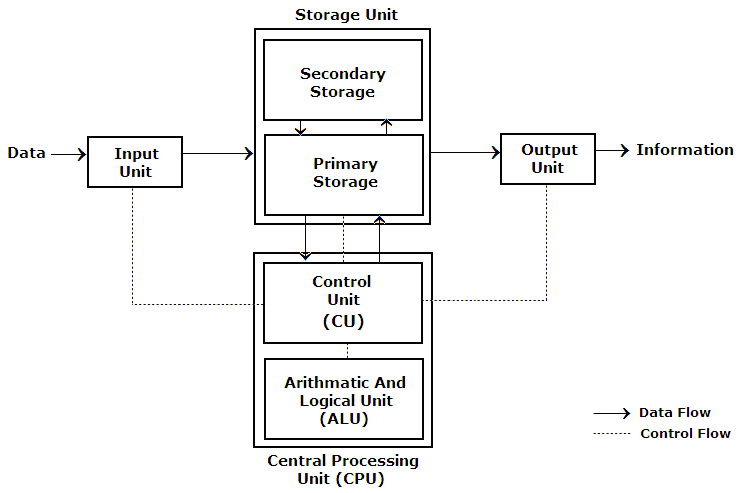
Organization implies structure & order. It is the arrangement of components that help to achieve objectives. For example a computer system.
The components of the computer system are:
(I) Input Unit
(II) Central Processing Unit
a. Memory Unit
b. ALU
c. Control Unit
(III) Output Unit
When linked together they work as a whole system for producing information. General arrangements of various units are:
-
Interaction:
Interaction refers to the manner in which each component functions with other components of the system.
For Eg. In a computer system, the CPU must interact with the input unit to solve a problem.
-
Interdependence:
Interdependence means that components of subsystems of the system depend on one another. One subsystem depends on the input of another subsystem for proper functioning.
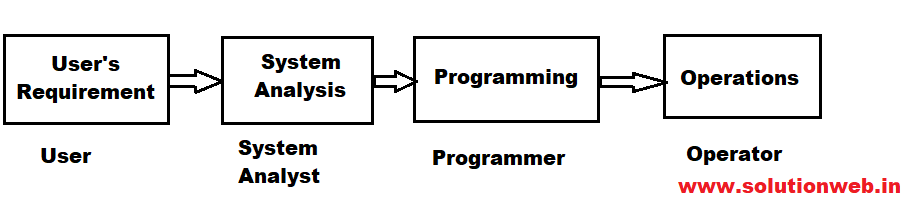
For Eg. A decision to computerize an application is initiated by the user, analyzed & designed by the analyst, programmed & tested by the programmer & run by the computer operator. None of these persons can perform properly without the required input from others in the computer-based system.
-
Integration:
Integration is concerned with how a system is tied together. It means that components of the system work together within the system even though each component performs a unique function.
-
Behavior
A system reacts to inputs from its environment & these responses determine its behavior.
For Eg. A person may look left & right before crossing a road.
-
Self- Regulating:
A system tends to maintain itself in a steady state.
-
Life Cycle:
Every system has its cycle of birth, life & death.